You may have taken a driving test and received a minor, or possibly a serious or dangerous fault for undue hesitation. So what exactly is undue hesitation?
The driving examiner may mark your test report under the section ‘Progress’ with the fault of ‘undue hesitation’. As you can probably gather, undue hesitation is where the test candidate is taking an unnecessarily long time to complete a task.
A test candidate can be marked for undue hesitation for varying circumstances such as moving off, moving away from traffic lights or a pedestrian crossing, but the vast majority of faults occur around junctions. Essentially, undue hesitation is a failure to proceed when it is safe to do so.
Is it a Test Failure?
Due to inexperience and uncertainty, learner drivers often hesitate to excess and with practice, hesitation decreases as skill, knowledge and confidence increase. However, nerves can cause a learner to drive differently during test conditions when compared to driving lessons. A question often asked by learner drivers – ‘is undue hesitation a fail?’ To answer whether undue hesitation results in a test failure or not depends on:
- how often the fault occurs – if the candidate repeats the fault, usually around three or more occasions, this is likely to result in a failure, though the specifics are down the the examiners judgement.
- how the fault impacts on other road users – if undue hesitation has caused another road user to take action; this could be that they sound their horn in frustration or drive around you for example, then just one instance of the fault will result in a serious or dangerous marking – resulting in a failure.
If the fault occurs once or twice, it is within moderate margins and does not cause other road users to take action, then it’s likely to be marked as a minor fault – though what defines a minor over a serious fault can vary to some extent on individual examiners.
How to Prevent Undue Hesitation
- Take sufficient lessons until you are confident in your abilities to move away from junctions of all types
- Take a mock test before your real test as this will help you prepare and may also aid in alleviating with nerves during the actual test
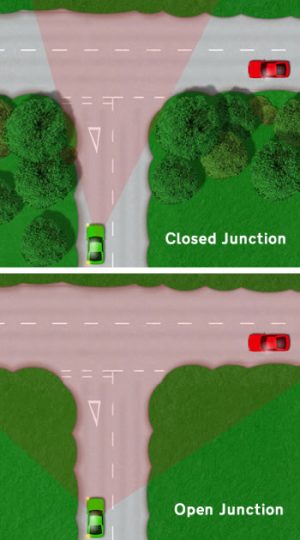
Test candidates that fail the driving test due to undue hesitation often do so because of a lack of observation and planning. This particular fault usually occurs around junctions, which include roundabouts and crossroads. Due to the candidate not applying enough observation and planning in advance, they’ll arrive at the junction and decide what to do once they are there – this is typically what leads to the undue hesitation.
What the test candidate should do is to observe and base their actions on what they see. At a T-junction for example, look for signs that inform you of a junction ahead- this may be give way or stop signs. Other clues could be buildings, fences or hedges that appear to run across the road, this indicates where the junction is.
As you approach, look where the junction line is (or where your road ends if there isn’t a junction line) but combine this with looking left and right to see how much of the new road you can see.
What you see here, determines your speed; if the junction is closed and you can see very little of the new road, approach very slowly and prepare to stop, if it is an open junction and you can clearly see the the new road is free from traffic, you can likely proceed onto the new road without the need to stop (unless there’s a stop sign).
Is Undue Hesitation Dangerous?
Many accidents occur due to undue hesitation for example, a driver approaching an open roundabout where it is clearly safe to proceed as there’s no traffic approaching from the right. Although it’s safe, the driver stops and the driver of the vehicle behind doesn’t anticipate the stop. This may result in a collision.
Further Information
For further information on open and closed junctions, see:

Will undue hesitation be assumed at traffic lights with cars that these days where the engine switches off due to the vehicle not moving? So now you have to go through the procedure of restarting it. I found this to be the case many times when I have been behind a car or a bus with this feature. It may only be seconds but it can make the difference of how many vehicles get through the situation. Plus it marvels me that people’s perception is different, example you may think when on foot it’s safe to cross the road whereas I may differ and may wait a little long. Does that make me a failure?? I don’t think so as it’s my body I’m dealing with. As long as the driver is aware and safe I don’t see what the problem is, except that people are in far too much of a rush today.
Hello Peter,
I think in your example of driving, you’re more talking about hesitation that’s out of your control. Undue hesitation would be for example, a test candidate waiting to move onto a roundabout, but has missed several opportunities where it was perfectly safe to go. These instances may become hazardous as it may result in other drivers becoming impatient and taking alternative actions to manoeuvre onto the roundabout, or perhaps attempting to overtake the test candidate at the earliest opportunity, further ahead where normally they might not. The instance of you crossing the road as a pedestrian wouldn’t be relevant because you would not affect others.
I do take your point of drivers being too impatient though. Drivers are also far less patient with learners than they once used to be. Seems to be an issue that’s worsening.