From pedestrians, cyclists and motorists, traffic lights are an integral part of our busy society, enabling our road systems to run smoothly.
How traffic lights work is in its simplest form a basic computer that is timed to change the lights. Timings are based on how much traffic passes through each day and timings may change at certain times of day (the busiest road gets a longer green light).
Advanced traffic lights have sensors that detect an approaching vehicle, especially useful for motorists driving at night where the sensor will trigger their light green, provided other routes are clear from traffic. These types of lights reduce congestion.
How traffic lights change
Traffic lights change in a certain sequence:
-
Amber
You must stop at an amber traffic light unless you’ve already crossed over the stop line or that you are so close that it may cause an accident with the vehicle behind.
-
Red
You must stop and wait behind the stop line.
-
Red and amber
Get prepared to go, but do not move until the green light shows.
-
Green
You may go, but only proceed if the way through the junction is clear.
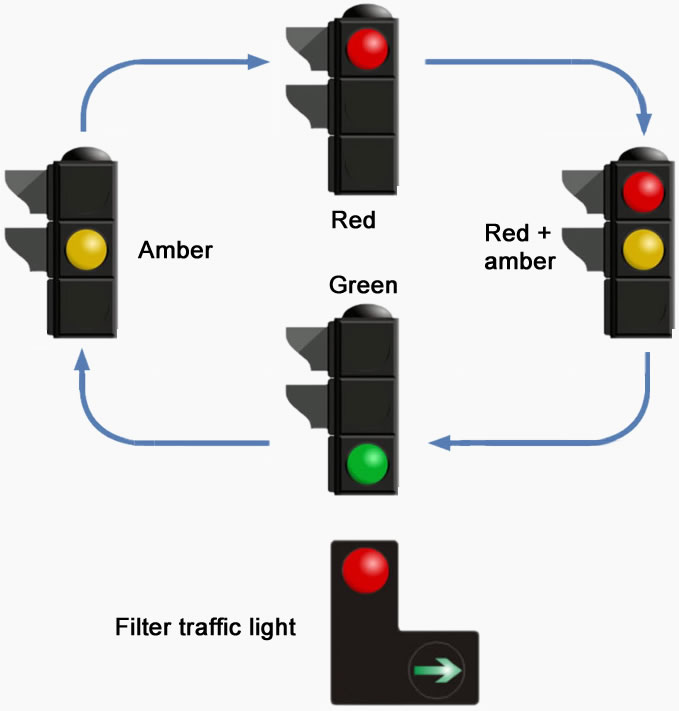
Traffic light filter arrow
Certain traffic lights may have a green filter arrow. If the filter arrow illuminates in the direction you are traveling, you can go even if the main light is on red.
Traffic lights that don’t work
Very occasionally you may come up against traffic lights that are out of order. There may or may not be a sign warning you in advance or when you arrive at the lights. At busy intersections a police officer may be deployed to control traffic until the lights are repaired.
If however no police officer is present, it’s important to understand that nobody has priority at traffic lights that do not work. Drive with extreme caution until you clear the junction.
Tram light signals
You may not live in an area that has trams. You still need to understand tram light signals in case you visit an area that has them. Tram questions are also part of the theory test. In areas where trams are in use, you may see traffic lights such as this one in the image. The light mounted to the right provides instructions to tram drivers.

Motorway light signals
Although currently learner drivers are not able to learn on motorways, you will still need to learn motorway rules and light signals for the theory test. Motorway light signals can be placed on overhead gantries or at the roadside.

Motorway amber light signals
Amber light signals warn motorists of a hazard. Examples can include reduced visibility due to fog or that the maximum speed limit has been reduced to 50mph.

MOTORWAY RED LIGHT SIGNALS
Red light signals above a lane informs a motorists that their lane has been closed and that they must move to another lane. Red light signals above all lanes, on the roadside or at the central reservation means you must stop and not go beyond the red lights. For further information, see motorways for signs, light signals, rules and regulations.
Related tutorials and guides on traffic lights
The tutorial below goes further into traffic lights and motorway light signals
