Section 4 of 14 of the DVSA driving theory test covers hazard awareness. The various types of hazards detailed in this section include static and moving hazards, hazards related to road and weather, plus hazards that can occur due to the driver not being fit to drive.
The hazard awareness section of the official DVSA theory test contains questions related to the hazards above. At the beginning of this section is revision material that should be read in preparation for the test.
After you have finished revision, there’s a practice quiz to test your knowledge at the bottom of this page. It’s not a mock test but more a revision quiz as the correct answer is provided after each question to help you revise.
Links are provided in this section for further reading but are not required for revising this category. Before we take the quiz, we shall cover some of the topics in the ‘hazard awareness’ category that will important revision for the DVSA theory test.
Static Hazards
There are many hazards that you’ll encounter whilst driving, some of these will be static and include:
- Hazards in the road such as parked cars and road works
- Junctions, roundabouts and crossroads
- Pedestrian crossings and level crossings
- Traffic lights
As you begin driving, you’ll be concentrating primarily on vehicle control. As you gain in experience, you’ll need to become more aware of hazards and spotting hazards early on. As you gain in experience, become more observant and become more aware of road signs and road markings that are often placed before hazards to alert you and to allow you to prepare.
Parked Cars
Parked cars represent a hazard, in particular when they are a parked illegally and where they pose a danger to the public. Such instances are where driver park on the white zig zag lines at pedestrian crossings. Always try to leave sufficient distance from parked cars whilst driving in case doors open and in busy areas in particular, be cautious of children running out from between them.
Road Works
Road works are required on any road type from time-to-time. Road works on dual carriageways and motorways represent a hazard due to the high speed of the roads.

If you see a hazard or road works on a dual carriageway or motorway that involves you reducing speed, you may briefly use your hazard warning lights to warn following drivers. If your vehicle breaks down, use your hazard warning lights to warn other motorists.
Where road works are located on dual carriageways or motorways, slow moving vehicles may be used to inform motorists of the hazard and to change lane. Yellow signs may also be used where road works are present.
Junctions, Roundabouts and Crossroads
Junctions, including roundabouts and crossroads can be particularly hazardous in urban areas. Be careful when pulling out of a junction that has tree, bushes, fences or parked cars obscuring the road you intend on entering. Move out slowly until you can see the road is clear. Be cautious of cyclists that can be obscured by your vehicle door post when moving out from a junction.
When parking, avoid parking too close to a junction and creating a hazard. At junctions or crossroads that are light controlled and where the lights have failed, treat this as an unmarked junction where no one has priority.
Moving Hazards
There are many moving hazards that you’ll encounter as a driver. Some of these are:
- Pedestrians – especially vulnerable whilst crossing the road at junctions and pedestrian crossings. Some pedestrians may take time to cross, always remain patient and allow them time. Be prepared to allow a safe passing distance on country roads where pedestrians may be walking without a pavement.
- Cyclists – with little protection and difficult to see are vulnerable. Give cyclists plenty of room when passing as they may swerve to avoid drains and potholes and may wobble in windy conditions. Check mirrors before making turns as a cyclist may be filtering down the side.
- Motorcyclists – can also be difficult to see. As with cyclists, check mirrors before making a turn as a motorcyclist may be coming alongside. Motorcyclists can easily be concealed in your mirror blind spot, so ensure you check this and your mirrors before changing lanes.
- Horse riders – horses can be unpredictable. Approach slowly and allow for plenty of room when overtaking.
- Large vehicles – such as buses often pull into stops. When a bus signals to exit the stop, stop to allow the bus exit if safe to do so. Be cautious of passengers exiting the bus to cross the road, in particular school children. Large and tall vehicles may require extra room when turning or may drive into the middle of the road when driving under a bridge. Large vehicles of 13 metres in length or more will have red and yellow markings on the rear.
Road and Weather Conditions
Always take into account weather conditions and prepare for them accordingly. Bright sunlight, especially in the winter when it is low in the sky can make roads difficult to see. This can be especially hazardous on wet roads that reflect light. Stopping distances are affected depending on weather conditions.
If it’s raining, double your normal distance from the vehicle in front to four seconds. In icy conditions, the distance should be extended to 20 seconds. Remember to use dipped headlights and illuminate your rear fog lamp in fog conditions.
Being a Hazard Yourself
Always be aware of what is around you. Your interior mirror provides an exact representation of what is behind you whilst the door mirrors are usually convex glass. Convex glass is curved to allow for a wider field of view.
Tiredness
Tiredness is a major cause of road accidents as if affects your ability to concentrate and reduces awareness. Avoid driving if you are tired. If whilst driving you begin to feel drowsy, open a window to allow in fresh air and if possible pull over in a safe and legal position to rest. If driving on a motorway, leave at the next exit to locate a suitable resting area.
Alcohol and Drugs
Always avoid driving if you have been drinking alcohol or under the influence of drugs (no matter how little). Certain medication or drugs prescribed by your doctor may cause drowsiness. Before taking, check the label or consult your doctor or pharmacist if unsure.
If you are unfit to drive due to alcohol or drugs and have been convicted, you’ll receive a substantial fine and penalty points on your licence. It’s likely that you’ll receive a driving ban and the cost of future car insurance premiums will increase significantly.
Concentration
Your concentration can be affected by:
- Using a mobile phone – turn off your mobile whilst driving or switch it to silent to avoid distraction
- Looking a the Sat-nav or traditional paper map – plan your route in advance and if you need to look at a map, find a safe and legal place to stop
- Road rage – we all make mistakes and sometimes this happens whilst driving. If a road user angers you, rather than retaliate, remain calm else you risk making the situation worse
THEORY TEST Hazard Awareness REVISION QUIZ
Take the theory test quiz for the category of ‘Hazard Awareness’, which number 4 of the 14 categories. The quiz provides 16 questions with the answers being provided immediately after you have answered.
Quiz-summary
0 of 16 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
Information
Take the theory Test Hazard Awareness Section Practice Revision Quiz
Certain questions may require more than one answer.
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 16 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 16
1. Question

Where would you see these hazard warning markers?
Correct
Incorrect
These red and yellow reflective markers make objects easier to see in the dark and inform of a hazard. They should be placed on vehicles 13 metres in length, large goods vehicles and skips that are placed on public roads.
-
Question 2 of 16
2. Question
Correct
Incorrect
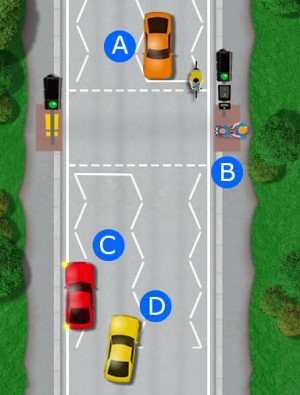
It is illegal to park on the white zigzag lines on pedestrian crossings. Red car ‘C’ is causing a hazard because it is:
- blocking the view of the road for pedestrians that wish to cross
- blocking the view of the crossing for other drivers
-
Question 3 of 16
3. Question
You are approaching a crossroads where the traffic lights have failed. You should:
Correct
Incorrect
A crossroads where the traffic lights have failed must be treated as though it is an unmarked crossroads. Be prepared to give way as no one has priority.
-
Question 4 of 16
4. Question
Mark two answers
You are driving on a dual carriageway following a lorry and it is raining. You should:
Correct
Incorrect
Under normal dry conditions, you should leave a two second gap between you and the vehicle in front. If the road is wet, this should be doubled to four seconds. Spray from vehicles, particularly large vehicles will reduce your vision. Keeping back will keep you out of the spray from the lorries tyres, will allow you more time to stop if needed, you’ll be able to see past the lorry and the lorry will be able to see you in their mirrors.
-
Question 5 of 16
5. Question
Door mirrors often use convex glass meaning that they are curved. What is the benefit of this?
Correct
Incorrect
Curved, or convex glass provides a wider field of vision. This does not eliminate blind spots however, so it’s essential before changing lanes or moving off that you look over your shoulder to check the relevant blind spot.
-
Question 6 of 16
6. Question

Up ahead in the middle of a three lane motorway, you see a slow moving lorry with this sign on the back. What should you do?
Correct
Incorrect
This sign is used on slow-moving or stationary road works vehicles. If you intend on overtaking the vehicle you may do so on the left.
-
Question 7 of 16
7. Question
Mark four answers
Drinking alcohol results in:
Correct
Incorrect
Just one drink could be enough to put you over the legal limit. So not to pose a danger to yourself and others, don’t risk it and remain alcohol free when driving.
-
Question 8 of 16
8. Question
If you are convicted of driving whilst unfit through drink or drugs, which of these is likely to rise considerably?
Correct
Incorrect
If convicted of driving whilst under the influence of drugs or over the legal limit of alcohol, it’s highly likely you’ll receive a driving ban and fine. Your car insurance is also likely to rise considerably.
-
Question 9 of 16
9. Question
You take cough medicine before driving. Before taking the medicine you should:
Correct
Incorrect
Before taking either over-the-counter or prescription drugs, you must check that they do not affect driving. Drugs may reduce awareness, perception and judgement.
-
Question 10 of 16
10. Question
Mark two answers
Whilst driving you begin to feel drowsy. What should you do?
Correct
Incorrect
When drowsy, you are at risk of falling asleep and your reaction times are slower. Pull over and find a safe place to rest.
-
Question 11 of 16
11. Question
Whilst driving along this road, from the left a driver is pulling out of their driveway. What should you do?
Correct
Incorrect
If a motorist is reversing into your path, slow down and be prepared to stop. If necessary, sound your horn.
-
Question 12 of 16
12. Question
Mark three answers
Which of these is often the result of drinking alcohol?
Correct
Incorrect
Alcohol will often increase an individuals confidence which results in them taking risks that they otherwise would not make.
-
Question 13 of 16
13. Question
Mark four answers
Other than alcohol, what else can seriously affect concentration?
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 14 of 16
14. Question
Your eyesight has become very poor and your optician is unable to help you. As a driver, you must inform:
Correct
Incorrect
Driving with poor eyesight seriously reduces judgement and concentration. If you are unable to meet the minimum eyesight legal requirements, you must inform the Driver and Vehicle Licensing Agency.
-
Question 15 of 16
15. Question
Mark two answers
It is raining and you are driving on a motorway following a lorry. You should:
Correct
Incorrect
In dry conditions you should allow at least a two second gap. This increases to four seconds in wet conditions. Staying well back from the vehicle in front allows you:
[ul type=info]
- To see past the vehicle
- To avoid spray from the lorries wheels
- More time to stop if you need to
- To be seen by the lorry driver in their mirrors
[/ul]
-
Question 16 of 16
16. Question
Mark two answers
As a provisional licence holder, you must not drive a car :
Correct
Incorrect
A learner driver must be supervised by a person who is at least 21 years old and has a valid driving licence, which they have held for at least three years. Learner drivers are now permitted to drive on motorways provided they are accompanied by a fully qualified driving instructor with dual controls.
THEORY TEST CATEGORIES
- Theory Test Alertness Revision and Test
- Theory Test Attitude Revision and Test
- Theory Test Documents Revision and Test